- ข่าวสารโรคมะเร็ง
- ■ อาการของโรคมะเร็งปอด
- ■ การวินิจฉัยโรคมะเร็งปอด
- ■ เทคโนโลยีสำหรับโรคมะเร็งปอด
- ■ เริองราวของผู้ป่วยมะเร็งปอด
- ■ ระยะของมะเร็งปอด
- ■ ผลการรายงานโรคมะเร็งปอด

จากข้อมูลสถิติที่กรมอนามัยโลกระบุ ในปี พ.ศ. 2557 ประเทศไทยพบผู้ที่ป่วยด้วยโรคมะเร็งปอดถึง 19,505 ราย เสียชีวิตไป 17,390 ราย ซึ่งเป็นอันดับ 1 ในการเสียชีวิตของคนไทย ถ้าอย่างนั้นมะเร็งปอดสามารถรักษาได้ไหม? การรักษาแบบบูรณาการที่มีผลข้างเคียงต่ำ บาดแผลเล็ก ผู้ป่วยฟื้นตัวเร็วสามารถช่วยให้ผู้ป่วยหลีกเลี่ยงการผ่าตัดและหลีกเลี่ยงความทรมานจากการให้ยาเคมีบำบัดในแบบเก่า และเพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการมีชีวิตอยู่ของผู้ป่วยให้ได้นานขึ้นอีกด้วย
หากท่านตรวจพบว่าป่วยเป็นโรคมะเร็งปอด เรายินดีช่วยเหลือ สามารถนัดออนไลน์หรือโทรนัดเพื่อติดต่อสอบถามได้ที่เบอร์:0610367888 0907099666
การแบ่งประเภทของมะเร็งปอด
มะเร็งปอดสามารถแบ่งออกเป็น 2 ประเภทใหญ่ได้ดังนี้ : มะเร็งปอดชนิดเซลล์ตัวโต Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (85%)และมะเร็งปอดชนิดเซลล์ตัวเล็ก Small Cell Lung Cancer(15%)มะเร็งปอดชนิดเซลล์ตัวโต แบ่งออกเป็น 3 ชนิดมะเร็ง คือ มะเร็งเซลล์squamous,มะเร็งเซลล์ adenocarcinoma และMast cell
การอธิบายเกี่ยวกับผลการรายงานทางการแพทย์ของมะเร็งปอด
1.มะเร็งเซลล์squamousและมะเร็งเซลล์ adenocarcinomaคือ?
2.ระดับความรุนแรงของมะเร็งปอดสามารถบอกอะไรได้บ้าง?
3.ในผลการรายงานการตรวจคำว่า” Immunohistochemistry ” คือ?
หากมีข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับผลพยาธิวิทยาของโรคมะเร็งปอด สอบถามออนไลน์หรือโทรปรึกษาแพทย์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญได้ทันที:0610367888 0907099666 พวกเรายินดีตอบข้อสงสัยของท่านทุกประการ!
อัตราการรอดชีวิตจากมะเร็งปอดในช่วงระยะเวลา 5 ปีมีดังนี้ :
มะเร็งปอดระยะที่ 4, น้อยกว่า 10%
เทคนิคการรักษาของมะเร็งปอด
ความเจ็บปวดจากการรักษาในแบบเก่า
การผ่าตัด : บาดแผลมีขนาดใหญ่ ความเสี่ยงสูงการให้ยาเคมีบำบัด : ผลข้างเคียงมาก เช่น ผมร่วง อาเจียนเป็นต้น
เทคโนโลยีการรักษามะเร็งปอดแบบใหม่ เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการมีชีวิตอยู่
การรักษาแบบบูรณาการ : บาดแผลมีขนาด 2-3mm. ผลข้างเคียงต่ำ เจ็บปวดน้อย
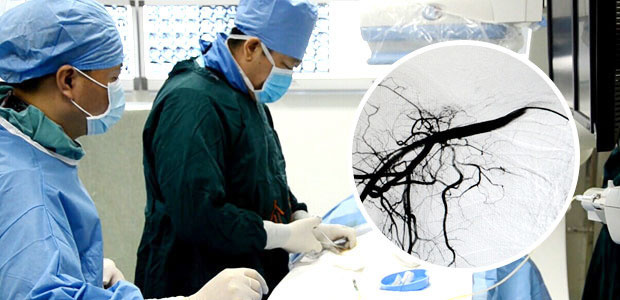
เทคนิคแบบเฉพาะจุด : บาดแผลขนาด 1 -2 mm. ใช้ยาต้านมะเร็งเข้าไปจู่โจมก้อนมะเร็งโดยตรง ความเข้มข้นของยามีมากกว่าการให้ยาเคมีบำบัดทางสายน้ำเกลือสูงถึง 2-8เท่า ผลข้างเคียงต่ำ มีความแม่นยำในการทำลายเซลล์มะเร็ง
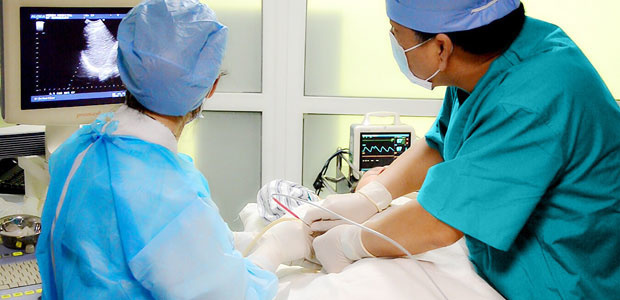
เทคนิคการใช้ความเย็น : บาดแผลเล็ก การรักษาตรงจุดเฉพาะที่ กระตุ้นภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกาย ลดภาวะการกลับมาเป็นซ้ำของมะเร็งปอด
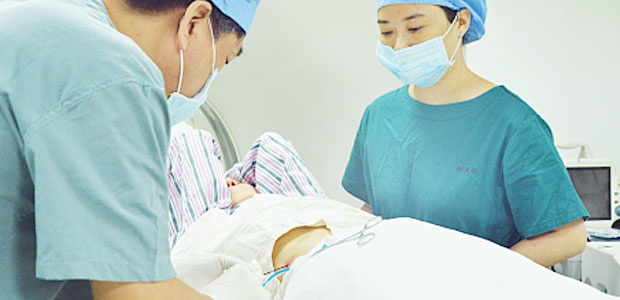
เทคนิคการใช้ความร้อน : บาดแผลมีขนาดเล็กเพียง 3mm. ประสิทธิภาพในการรักษามีสูง ระยะเวลาในการรักษาสั้น โดยปกติจะใช้เวลาอยู่ที่ 10 นาทีในก้อนมะเร็งขนาด 6CM. มีความปลอดภัยสูง ไม่มีผลข้างเคียงใดๆ อัตราการกลับมาเป็นซ้ำต่ำ

เทคนิคธรรมชาติบำบัด
เทคนิคธรรมชาติบำบัด : เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการสร้างภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกาย ลดความเสี่ยงในการแพร่กระจายและกลับมาเป็นซ้ำ ปลอดภัย ไม่มีผลข้างเคียงในการรักษา

เทคนิคแบบบูรณาการแพทย์แผนจีนและตะวันตก
เทคนิคแบบบูรณาการแพทย์แผนจีนและตะวันตก : ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการรักษา ลดภาวะผลข้างเคียงจากการรักษา ลดภาวะแทรกซ้อน ฟื้นตัวเร็ว ขยายระยะเวลาในการมีชีวิตทั้งที่ยังมีเนื้อร้ายอยู่
เทคโนโลยีในการรักษามะเร็งปอดเพิ่มเติม
หากอยากทราบว่าคุณเหมาะสมกับวิธีการรักษาแบบใด พวกเรายินดีให้ความช่วยเหลือ นัดออนไลน์หรือโทรสอบถามเพิ่มเติมเพื่อติดต่อเราได้ที่เบอร์: 0610367888 0907099666
ทีมแพทย์ MDT พร้อมให้คำปรึกษากับผู้ที่ป่วยด้วยโรคมะเร็งปอด วางแผนการรักษาเฉพาะบุคคล

หากมีข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับโรคมะเร็ง แนวทางการรักษา สามารถกรอกข้อมูลด้านล่างส่งมาหาเราหรือโทรปรึกษาแพทย์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญได้ทันที:0610367888 0907099666 พวกเรายินดีตอบข้อสงสัยของท่านทุกประการ!
แบบฟอร์มจองคิวเข้าปรึกษา
การดูแลผู้ที่ป่วยมะเร็งปอดและโภชนาการ
การดูแลผู้ป่วยเมื่อมีอาการคลื่นไส้อาเจียน
ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างอาหารการกินกับโรคมะเร็ง
ติดตามข้อมูลข่าวสารและเกร็ดความรู้ดีๆจากเราได้ที่
หากมีข้อสงสัย สามารถสอบถามเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
*หมายเหตุ : ผลลัพธ์จะขึ้นอยู่กับสภาพร่างกายของแต่ละบุคคล

*ประกาศ : การผ่าตัดจะให้ผลลัพธ์ที่ค่อนข้างดีต่อมะเร็งระยะแรก ที่เป็นมะเร็งชนิดเป็นก้อน (Solid Tumor) แต่อาจจะไม่เหมาะในการใช้กับมะเร็งระยะสุดท้าย สำหรับผู้ป่วยระยะกลาง ไปจนถึงระยะสุดท้ายที่มีภูมิต้านทานในร่างกายต่ำ เทคโนโลยีแบบบาดแผลเล็ก บูรณาการร่วมกับการคีโมและการฉายแสง จะช่วยเสริมสร้างภูมิต้านทานและลดผลกระทบที่อาจจะเกิดขึ้นกับผู้ป่วย ช่วยให้ผู้ป่วยได้รับผลลัพธ์ที่ดีมากยิ่งขึ้น